CS50X Week 10 Lecture Notes
Cybersecurity
brute-force attack
4-digit password, 10^4 or 10,000 possible combinations.
4-digit brute-force
from string import digits
from intertools import product
for passcode in product(digits, repeat=4):
print(passcode)
4-ascii_letter password, 52^4 or 7,311,616 possible combinations. 4-ascii_letters brute-force
from string import ascii_letters
from intertools import product
for passcode in product(ascii_letters, repeat=4):
print(passcode)
8-ascii_letter, digit, and punctuation password, 94^4 or 6,095,689,385,410,816 possible combinations. 8-ascii_letters, digit, punctuation brute-force
from string import ascii_letters, digit, punctuation
from intertools import product
for passcode in product(ascii_letters + digit + punctuation, repeat=8):
print(passcode)
Hashing
- One-way hashing allows online services to actually never store the original password typed by the user: Only the hashed value of these passwords. Accordingly, if there is a breach, only the hashed value will be known.
- Rainbow tables are huge dictionaries that adversaries use to attempt to pre-hash possible passwords as a means by which to attempt to break the hash algorithm.
- As an additional process to heightened security, programmers may sometimes introduce salting where it becomes unlikely that multiple users may have the same hash value to represent their passwords. You can imagine this as follows:
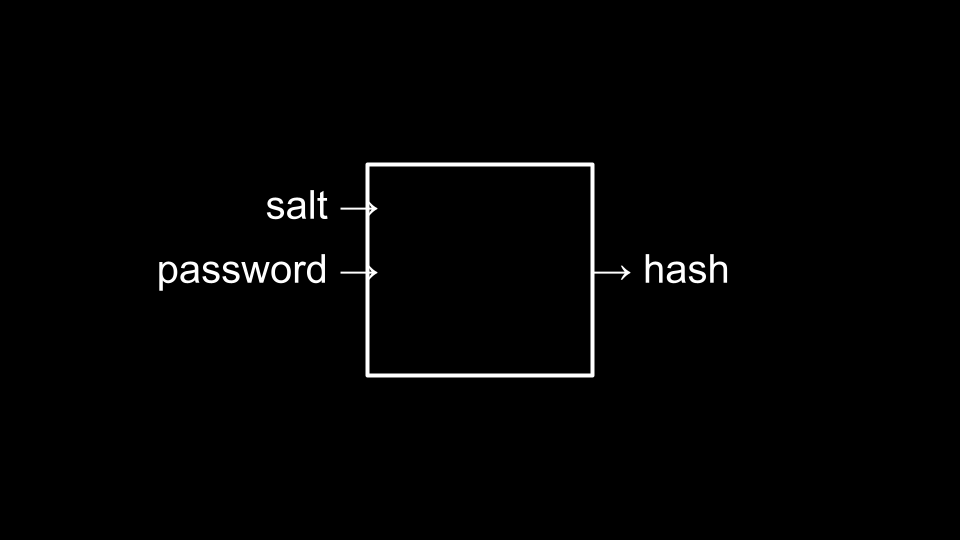
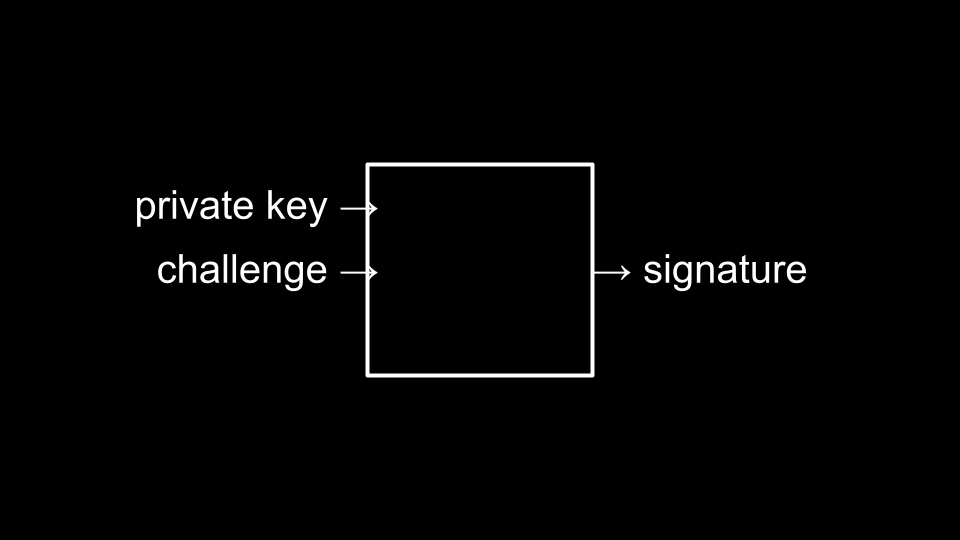
Passkeys
end-to-end encryption
- Think Signal
- Zoom offers it as a default setting
Deletion
- Secure Deletion
- rewrite drive
Full Disk encryption
- Protects against hard drive reading.
- ransomware is the negative side.