Professor Messer CompTIA Security+ 1.0 General Security Concepts
1.1 Compare and contrast various types of security controls
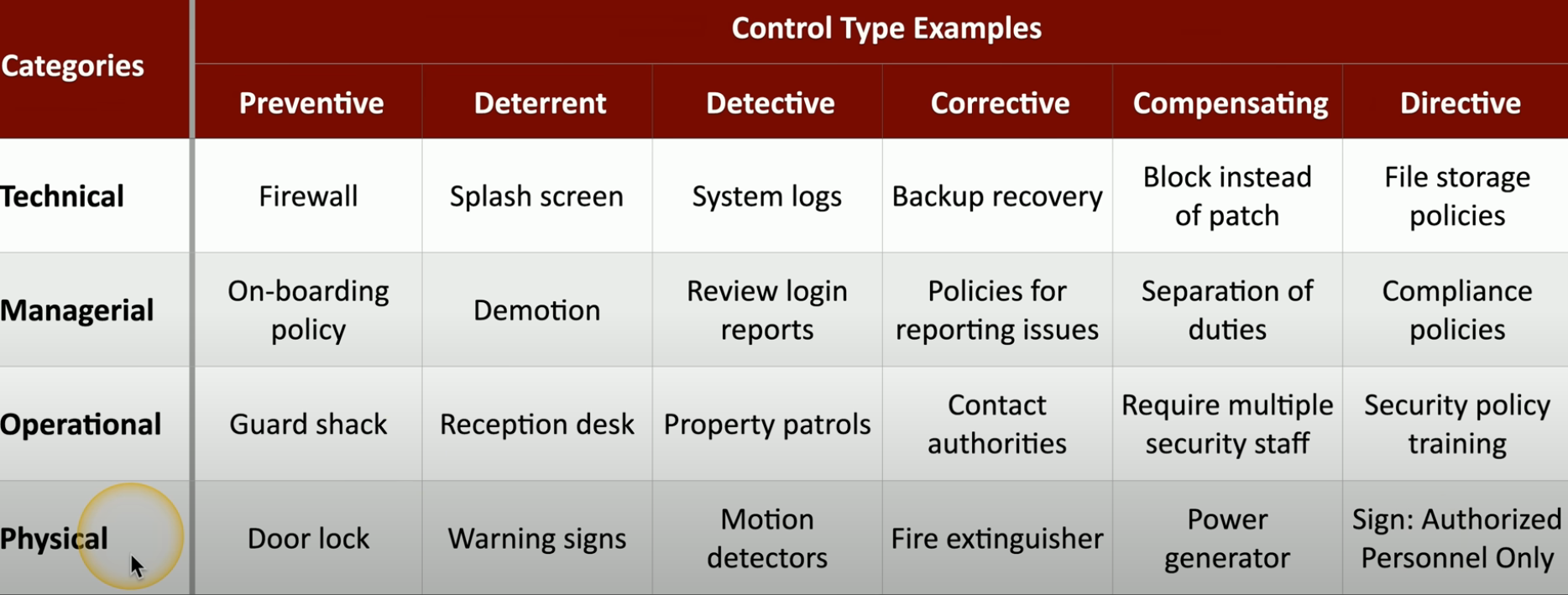
Control Categories
Technical Controls
- Firewalls, anti-virus Managerial controls
- Security policy Operational Controls
- Security Guards
- Password training guide Physical Controls
- Fences, locks
- Badge Readers
Control Types
- Preventative
- Deterrent
- Warning signs
- Detective
- Identify if and when breach occurs
- Corrective
- Applied after the event
- Restore from backups after ransomware
- Compensating
- Firewall blacks app until fixed
- Generator used for power outage
- Directive - Require employees to store data in encrypted drive. - “Authorized Personal Only”
1.2 Summarize fundamental security concepts.
The CIA Triad
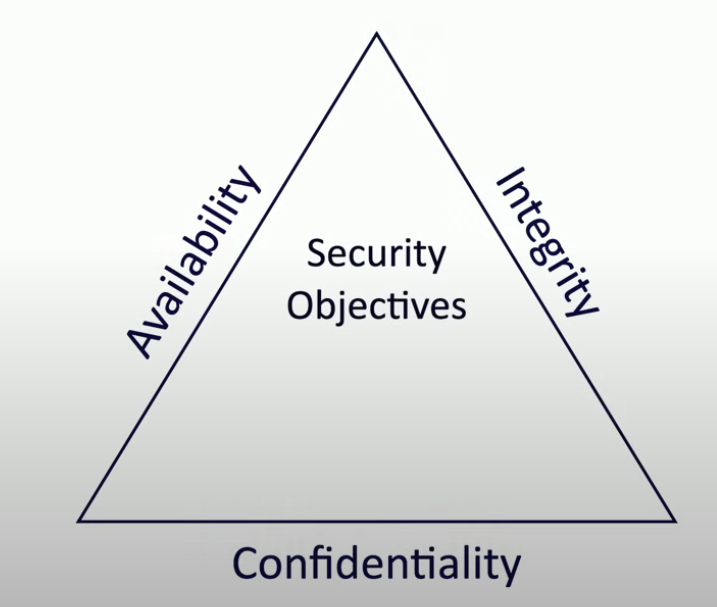 Also, AIC triad.
Also, AIC triad.
Security Objectives
- Availability
- Integrity
- Confidentiality
Encryption and Authentication.
Hashing ensures that our data matches both ends.
Digital signature: Encrypt the Hash.
Non-repudiation
- Proof of integrity
- Proof of origin
(Get-FileHash .. -A SHA256).hash -eq "HASH#"
Integrity
- Prove the message has not changed Authentication
- prove the source of the message Non-repudiation
- Make sure the signature isn’t fake
- Sign with a private key; paired with a public key.
AAA framework
- Identification
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Accounting
CA (Certificate Authority)
- Manage certificates for devices and users
- CA is a hashing and encryption algo?
Authorization Model
The relationship of groups and users
Gap Analysis
- Where we “are”
- Where we “want to go”
Determine end goal
- NIST Special Publication 800-171 R2
- ISO/IEC 27001
NIST National Institute of Standards & Technology ISO International Standards Organization
GAP REPORT EXAMPLE

Zero Trust
Authenticate each time you want to use a device, process, or user.
Planes of operation
- Split the network into functional planes
Data Plane
- process the frames, packets, and network data
- processing, forwarding, trunking, encrypting, NAT
NAT Network Address Translation
Control Plane
- Manages the actions of the data plane
- Define policies and rules
- Determines how packets should be forwarded
- Routing tables, session tables, NAT tables
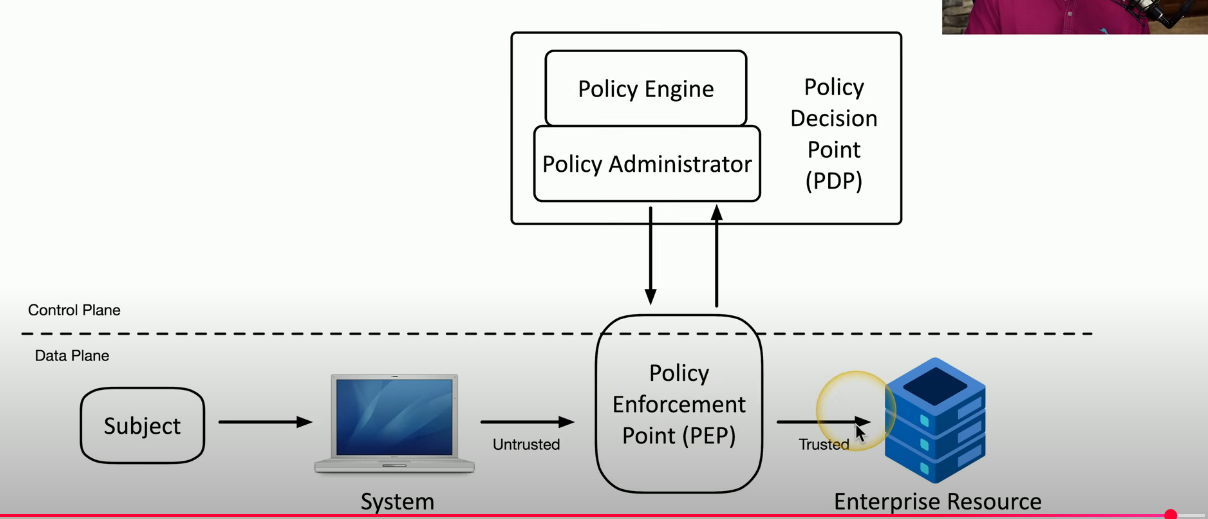
Policy-driven access control
PEP Policy Enforcement Point
- Where/the physical device, that allows traffic to move forward based upon the policies of the organization.
- Gatekeeper PDP Policy Decision point
- The actual machine with the rules.
Physical Security
- Access Control Vestibules
- Barriers
- Keycard access doors
Deception and Disruption
- Use a honeypot to keep them active and learn about the attackers
- Honeynets are when you build up entire faked networks (multiple honeypots)
- Honeyfiles are the fake files that appear top secret (passwords.csv)
- Honeytokens are the fake credentials that verify the honeynet has been hit.
1.3 Explain the importance of change management processes and the impact to security.
Change Management
- Upgrade software
- set on a defined timeline
Change Approval Process
- What
- When
- Where
- Why
Stakeholders are usually the best choice for taking ownership of the change process.
Impact Analysis
- Risk of changing, or not changing - Low - Medium - High Test in a sandbox environment.
- Create and Test backup process.
Covered in SOP (Standard Operating Procedue)
Technical Change Management
Allow List/Deny List
- Core tool for IT group controls
DOWNTIME is our responsibility.
- Learn the legacy application and document it to become the core expert.
- Ongoing documentation is a must!
Version Control allows us to maintain what app on what dependencies.
1.4 Explain the importance of using appropriate cryptographic solutions.
Public Key Infrastructure
PKI Public Key Infrastructure Digital certificates
Symmetric encryption
The same key is used for encryption and decryption
- Offers speed advantages
Asymmetric encryption
- Public key, private key (example bitcoin)
- public can encrypt
- private only can decrypt
- PGP Pretty Good Privacy
- GPG Gnu Privacy Guard
Encrypting Data
Protected data on storage devices
- Data at rest
Transport Encryption
- HTTPS
- VPN, SSL
Encryption Algorithms
DES Digital Encryption Standard
- 5 steps AES Advanced Encryption Standard AES-256 Advanced Encryption Standards 256-bit
- 3 steps encryption first, with multiple level choice
Cryptography keys are hidden, but the algo is public knowledge.
Key stretching
nesting the encryption like Russian Dolls
Key Exchange
- Out-of-Band key exchange
- exchange outside of the internet
- in-band key exchange
- exchange over the internet
- Public key cryptography
Encryption Technologies
TPM Trusted Platform Module
- cryptography and random number generation
HSM Hardware Security Module
- a TPM for an entire cluster of devices
- allows for faster encryption and decryption
- Pairs with a key manager software
Secure enclave
- a hardware processor that manages security of the system
Obfuscation
Steganography
- hiding the text inside a .jpeg Embedded messages in TCP packets
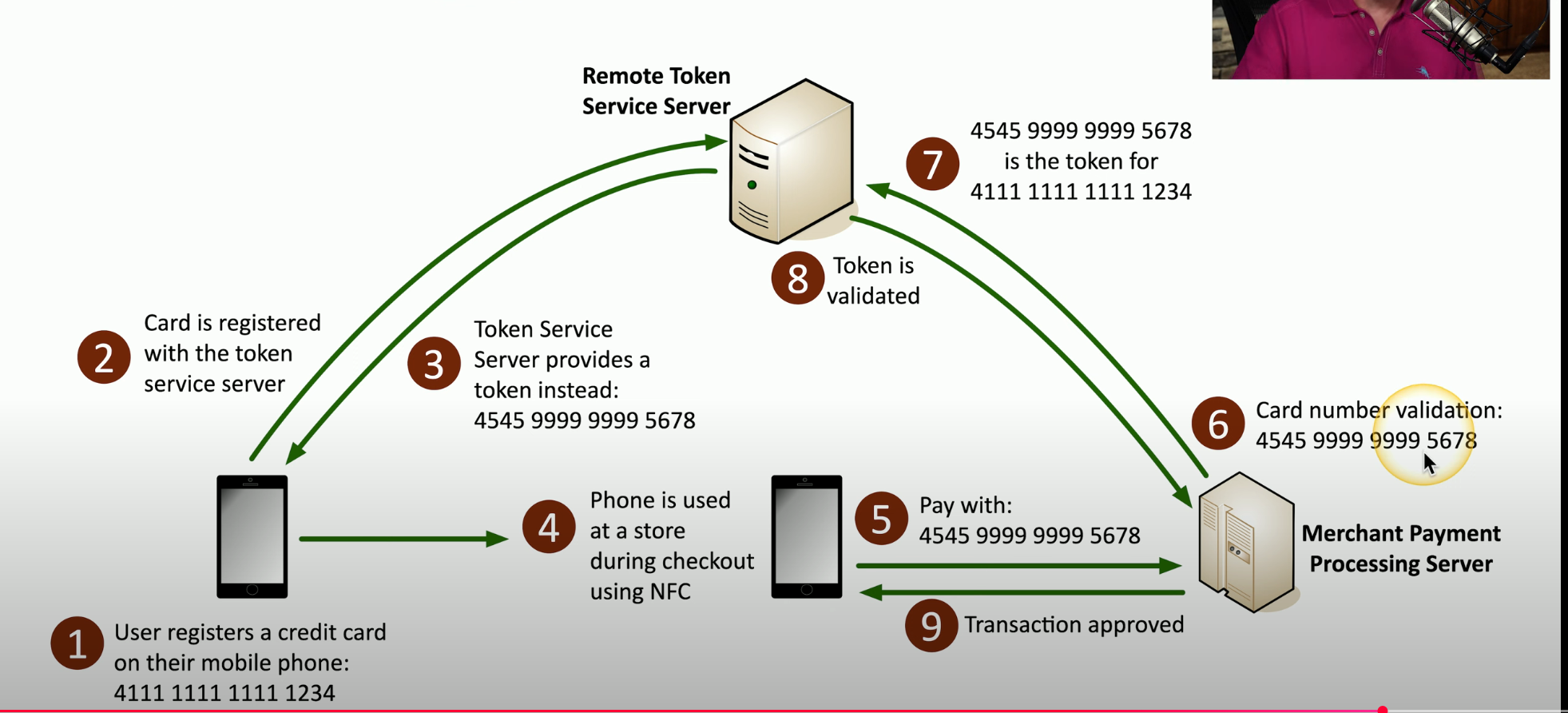
Tokenization
- Using a single use hash token from a credit card can go over the network openly, because it will only exist once.
Data masking
- hiding all but the last four of a credit card, or bank account number.
Hashing and Digital Signatures
Hashes
- Represent data a short string of text.
- A digital fingerprint
- Impossible to recover the original message form the digest
- Verify a downloaded document
- Digital signature
- Authentication, non-repudiation, and integrity
SHA256
- 256 bits / as 64 hexadecimal characters
Collision
- where hashes match but original data does not.
- MD5 found in 1996 to have collision issues.
Practical hashing
- Verify a downloaded file
(Get-FileHash .. -A SHA256).hash -eq "HASH#"
- Password storage vault
- Hash plus a salted hash
Salt
- random data based on each user
- Rainbow Tables
- backwards engineers the hash table, when not salted.
Digital Signature
- private key to encrypt
- public key to decrypt
- Can also work the other way around
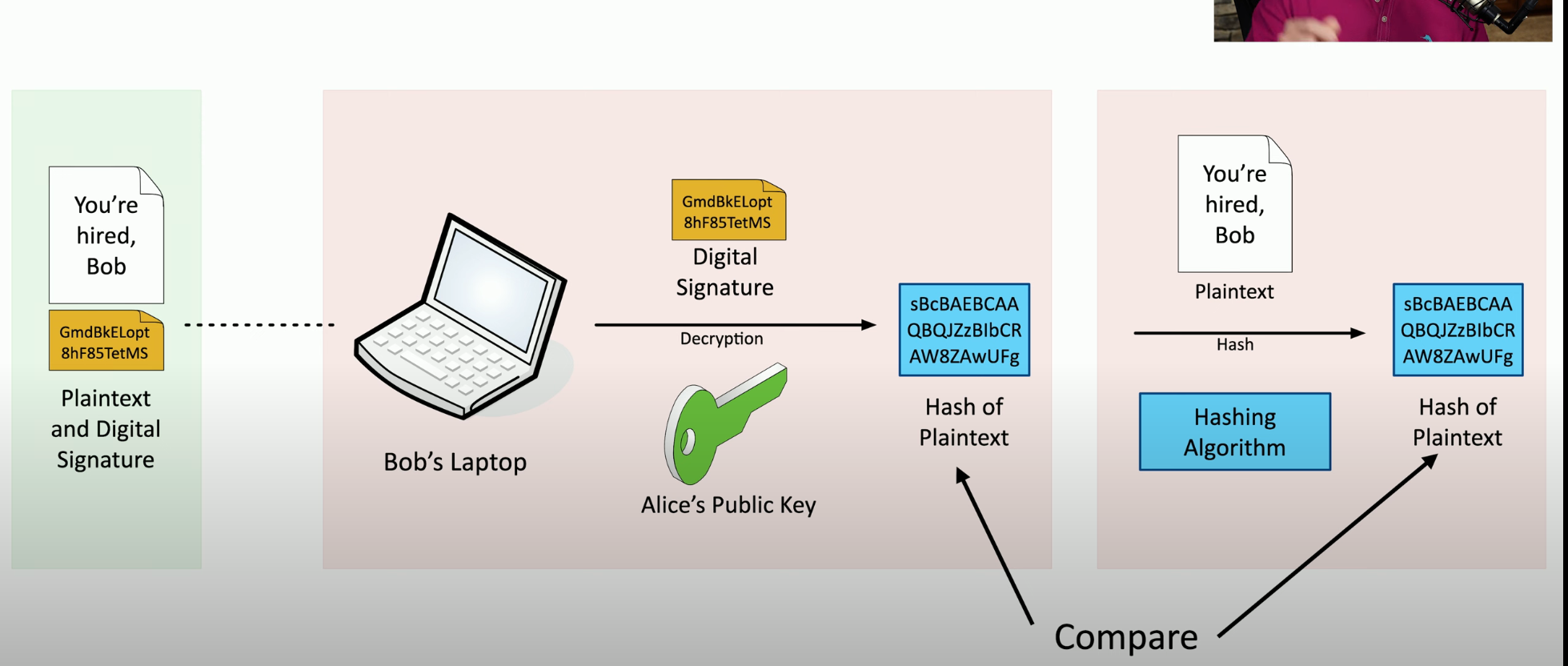
Creating a digital signature

Verify signature
Blockchain Technology
A Distributed Ledger
- Open Source ledger information.
- As long as no party gains 50% control, the blockchain remains immutable.
Certificates
- A public key certificate
- A digital signature
- PKI uses Certificate Authorities for additional trust.
- PKI Public Key Infrastructure
- CA Certificate Authority
- PKI uses Certificate Authorities for additional trust.
- Certificate creation can be built into the OS
- Windows Domain services
- X.509
- standard website certificate
Root of Trust
- IT security requires trust
- The trusted source that we rely on (e.g. MS Windows)
- website CA when we visit the website.
Private Certificate Authorities
- for internal network software
- Windows Certificate Services
- OpenCA
- Internal CA process is same as an external CA
Wildcard Certificates
*.google.com- the
*means any subdomain would be valid under the certificate.
- the
Key revocaiton
- CRL Certificate Revocation List
- a centralized way to revoke certificates across a network
- Built into a CA
OCSP stapling
- OCSP Online Certificate Status Protocol
- provides scalability for OCSP checks
- the CA is responsible for responding to all OCSP requests
- OCSP status is “stapled” into the SSL/TLS handshake.
- SSL Secure Sockets Layer
- TLS Transport Layer Security
- Most modern browsers support OCSP
Resources:
CompTIA Security+ Certificate Exam Objectives: SY0-701